Cloud computing uses server virtualization true or false quizlet – Cloud computing uses server virtualization true or false quizlet? That’s the million-dollar question, right? Seriously though, understanding the relationship between cloud computing and server virtualization is key to grasping how the modern digital world actually
-works*. This isn’t some stuffy textbook lecture; we’re diving into the nitty-gritty of how companies like Netflix and Amazon keep their services running smoothly.
We’ll explore the core concepts, tackle some true/false questions (think pop quiz!), and even look at real-world examples. Get ready to level up your cloud knowledge!
We’ll cover the basics of cloud computing models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS – yeah, those acronyms!), how virtualization boosts efficiency, and the major benefits of using virtualized servers in the cloud. Think of it as a crash course in cloud infrastructure, but way more fun than your intro to CS class. We’ll even break down some potential challenges and best practices, so you can sound like a total pro at your next tech meetup.
Defining Cloud Computing and Server Virtualization
Cloud computing and server virtualization are foundational concepts in modern IT infrastructure, deeply intertwined and essential for understanding the digital landscape. This section will define these concepts, explore their relationship, and examine different cloud models.Cloud computing fundamentally shifts computing resources – servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence – from a company’s on-premises data center to a network of remote data centers, typically owned and managed by a third-party provider.
This allows businesses to access and use these resources on demand, paying only for what they consume, much like a utility service. The flexibility and scalability offered are significant advantages.
Cloud Computing Models
The various cloud computing models offer different levels of control and responsibility. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate model for specific needs.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS provides fundamental computing resources, including virtual machines, storage, and networking. The user is responsible for operating systems, applications, and data. Think of it as renting a bare-bones server; you manage everything else. Examples include Amazon EC2, Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines, and Google Compute Engine.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS offers a complete development and deployment environment, including operating systems, programming languages, databases, and web servers. The user focuses on application development and deployment; the provider manages the underlying infrastructure. Heroku, Google App Engine, and AWS Elastic Beanstalk are examples of PaaS offerings.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS provides ready-to-use software applications over the internet. The user simply accesses and uses the application; the provider manages everything. Examples include Salesforce, Gmail, and Microsoft Office 365.
Server Virtualization
Server virtualization is the process of creating multiple virtual servers on a single physical server. This is achieved through virtualization software, which creates isolated environments, called virtual machines (VMs), each with its own operating system and resources. This allows for efficient resource utilization, improved flexibility, and enhanced disaster recovery capabilities. A single physical server can host numerous VMs, consolidating workloads and reducing hardware costs.
Server Virtualization’s Enhancement of Cloud Computing Efficiency
Server virtualization is a cornerstone of efficient cloud computing. By allowing multiple virtual servers to run on a single physical server, cloud providers can significantly reduce hardware costs and energy consumption. This leads to:
- Increased Resource Utilization: VMs can be easily created and destroyed as needed, ensuring that resources are used efficiently and only when required.
- Improved Scalability: Adding more VMs is much faster and simpler than adding physical servers, allowing for quick scaling of resources to meet fluctuating demands.
- Enhanced Flexibility: VMs can be easily migrated between physical servers, providing high availability and resilience.
- Reduced Hardware Costs: Consolidating multiple servers onto fewer physical machines drastically lowers capital expenditure.
Quizlet-Style Questions and Answers on the Topic
This section provides a series of true/false and multiple-choice questions designed to test your understanding of server virtualization within the context of cloud computing. These questions cover key concepts and practical applications, helping solidify your knowledge. Accurate understanding of these concepts is crucial for anyone working with or studying cloud technologies.
True/False Questions on Server Virtualization in Cloud Computing
The following table presents five true/false questions regarding server virtualization’s role in cloud computing, along with detailed explanations and supporting details for each answer. Understanding these nuances is key to grasping the efficiency and scalability of cloud infrastructure.
| Question | True/False | Explanation | Supporting Detail |
|---|---|---|---|
| Server virtualization allows multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical server. | True | This is the fundamental principle of server virtualization. It enables efficient resource utilization by sharing hardware resources among multiple VMs. | This leads to significant cost savings by reducing the need for numerous physical servers. A single physical server can host dozens, even hundreds, of VMs depending on its resources and the VMs’ demands. |
| Server virtualization is not relevant to cloud computing. | False | Server virtualization is a cornerstone technology of cloud computing. Cloud providers rely heavily on virtualization to provide scalable and on-demand resources. | Without virtualization, the scalability and flexibility of cloud services would be severely limited. The ability to quickly provision and de-provision VMs is a direct result of server virtualization. |
| Virtual machines in a cloud environment are completely isolated from each other. | False | While VMs are largely isolated, they share underlying physical hardware resources, and some level of resource contention is possible. Security measures are crucial. | Hypervisors manage resource allocation, but complete isolation is not always guaranteed, especially with resource-intensive VMs. Proper configuration and security practices are essential to prevent interference. |
| Server virtualization reduces energy consumption compared to using multiple physical servers. | True | Consolidating multiple VMs onto fewer physical servers directly translates to lower energy consumption and a smaller carbon footprint. | Fewer servers mean less hardware to power and cool, resulting in significant energy savings for both cloud providers and users. This is a major environmental benefit. |
| Hypervisors are not necessary for server virtualization. | False | Hypervisors are the software layer that manages and controls the virtual machines, allocating resources and ensuring their operation. | Without a hypervisor, it would be impossible to create and manage virtual machines. They are the essential component that enables server virtualization. Examples include VMware vSphere, Microsoft Hyper-V, and Xen. |
Multiple-Choice Questions on Server Virtualization and Cloud Computing
This section presents five multiple-choice questions that delve deeper into the interplay between server virtualization and cloud computing. Carefully consider each option before selecting your answer. Understanding these concepts will enhance your overall comprehension of cloud infrastructure.
For each question, select the best answer from the provided options.
- Question 1: What is the primary benefit of using server virtualization in cloud computing?
- Increased hardware costs
- Reduced resource utilization
- Improved scalability and flexibility
- Decreased security
Answer: Improved scalability and flexibility. Server virtualization allows for the dynamic allocation and deallocation of resources, making cloud services highly scalable and flexible to meet changing demands.
- Question 2: Which of the following is NOT a common hypervisor?
- VMware vSphere
- Microsoft Hyper-V
- Oracle VirtualBox
- Apache Tomcat
Answer: Apache Tomcat. Apache Tomcat is a servlet container, not a hypervisor. The others are all well-known hypervisors used in server virtualization.
- Question 3: What is a key security concern related to server virtualization in the cloud?
- Increased energy consumption
- Lack of scalability
- Potential for VM escape vulnerabilities
- Reduced cost savings
Answer: Potential for VM escape vulnerabilities. A compromised VM could potentially gain access to the underlying host system or other VMs if security measures are inadequate.
- Question 4: How does server virtualization contribute to cost savings in cloud computing?
- By requiring more physical servers
- By increasing energy consumption
- By consolidating multiple VMs onto fewer physical servers
- By reducing available resources
Answer: By consolidating multiple VMs onto fewer physical servers. This reduces the need for numerous physical servers, leading to lower hardware, energy, and maintenance costs.
- Question 5: Which of the following best describes a “type 1” hypervisor?
- Runs on top of an existing operating system
- Runs directly on the hardware
- Is a type of cloud storage service
- Is a type of network security device
Answer: Runs directly on the hardware. A type 1 hypervisor, also known as a bare-metal hypervisor, runs directly on the server’s hardware, providing a more efficient and secure virtualization environment compared to type 2 hypervisors.
Illustrative Examples of Cloud Computing Using Server Virtualization: Cloud Computing Uses Server Virtualization True Or False Quizlet
Server virtualization is a cornerstone of modern cloud computing, allowing for efficient resource allocation and scalability. Its widespread adoption across various industries demonstrates its significant impact on operational efficiency and cost savings. Let’s explore some real-world examples.
Real-World Examples of Server Virtualization in Cloud Computing
Several major companies leverage server virtualization extensively in their cloud infrastructures. These examples highlight the diverse applications and benefits of this technology.
- Netflix: Netflix relies heavily on cloud computing and server virtualization to deliver its streaming service globally. By virtualizing their servers, they can dynamically scale their infrastructure to handle fluctuating demand, ensuring smooth streaming during peak viewing times like holidays or new release launches. This scalability reduces infrastructure costs by only paying for the computing power needed at any given moment, avoiding the expense of maintaining always-on, over-provisioned hardware.
They also benefit from increased resilience and fault tolerance; if one virtual machine fails, others can seamlessly take over, minimizing service disruptions.
- Amazon (AWS): As the leading cloud provider, Amazon Web Services (AWS) uses server virtualization extensively within its own data centers. AWS offers various virtual machine instances (like EC2) based on virtualized servers. This allows customers to access computing resources on demand, paying only for what they use. The virtualization layer allows AWS to efficiently manage and allocate resources across its massive infrastructure, maximizing utilization and minimizing costs.
This efficiency is key to AWS’s competitive pricing and scalability.
- Salesforce: Salesforce, a leading CRM provider, uses server virtualization to support its cloud-based applications. Virtualization allows them to rapidly deploy new features and updates, respond quickly to customer needs, and efficiently manage their massive customer data. By leveraging virtualized environments, Salesforce can easily scale its infrastructure up or down to meet fluctuating demand, ensuring high availability and performance for its global customer base.
This also improves their disaster recovery capabilities by allowing them to easily replicate and failover virtual machines to different data centers.
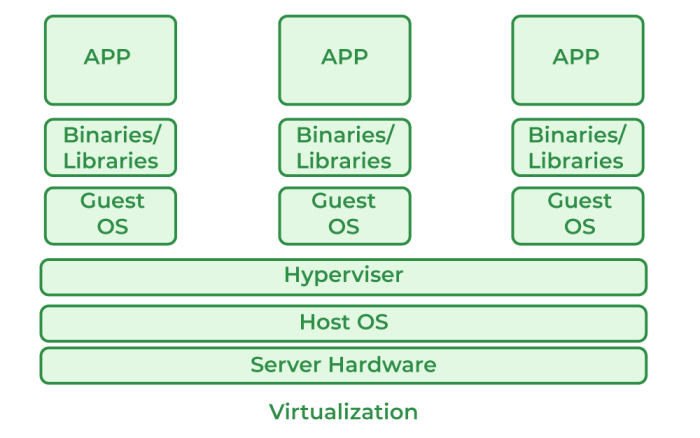
Virtual Machine Architecture within a Cloud Data Center
Imagine a powerful physical server (the “bare metal”) within a cloud data center. This server is managed by a hypervisor, a software layer that creates and manages virtual machines (VMs). Each VM is essentially a virtualized copy of a physical server, with its own isolated operating system, applications, and resources. The hypervisor allocates resources—CPU, RAM, storage, and network—from the physical server to each VM as needed.
The VMs run independently, unaware of each other’s existence, providing isolation and security. This allows multiple applications and operating systems to run concurrently on a single physical server, optimizing resource utilization and reducing hardware costs. The hypervisor also handles tasks like resource scheduling, memory management, and I/O operations for all VMs. Think of it as a sophisticated apartment building manager, allocating resources to tenants (VMs) while ensuring fair usage and preventing conflicts.
Scaling Cloud Resources Using Server Virtualization, Cloud computing uses server virtualization true or false quizlet
Let’s say an e-commerce company anticipates a surge in traffic during a major sale. Using server virtualization, they can efficiently scale their cloud resources to handle the increased demand.
- Monitoring: The company continuously monitors its cloud infrastructure’s performance metrics, including CPU utilization, memory usage, and network traffic.
- Prediction: Based on historical data and anticipated sales, the company predicts the increase in demand and the required additional resources.
- Automated Scaling: They configure their cloud environment (e.g., using AWS Auto Scaling or similar services) to automatically launch additional virtual machines when certain thresholds are reached (e.g., CPU utilization exceeding 80%). These new VMs are pre-configured with the necessary applications and software.
- Resource Allocation: The hypervisor dynamically allocates resources from the underlying physical servers to the newly launched VMs. This ensures that all requests are handled efficiently.
- Load Balancing: A load balancer distributes incoming traffic across all active VMs, preventing any single VM from becoming overloaded. This ensures consistent performance for all users.
- Post-Peak Scaling: Once the peak demand subsides, the automated scaling system automatically terminates the extra VMs, reducing costs by only paying for resources actually used.
This process demonstrates how server virtualization enables on-demand scalability, a key benefit of cloud computing. The ability to quickly and efficiently add or remove resources as needed allows companies to optimize costs while ensuring high availability and performance.
So, does cloud computing use server virtualization? The answer is a resounding YES! We’ve explored the fundamental connection between these two technologies, seeing how virtualization allows for efficient resource allocation, scalability, and cost savings. From understanding the different cloud models to tackling some quizlet-style questions, we’ve covered the essentials. Remember, this isn’t just theoretical; it’s the backbone of how many of the services you use every day operate.
Now go forth and impress your friends with your newfound cloud computing prowess!
Question Bank
What are some common security concerns with server virtualization in the cloud?
Security is a big deal! Concerns include unauthorized access to virtual machines, data breaches, and the potential for hypervisor vulnerabilities. Proper security measures like strong passwords, firewalls, and regular security audits are crucial.
How does server virtualization impact cost savings in cloud computing?
Virtualization lets you consolidate multiple servers onto fewer physical machines, reducing hardware costs, energy consumption, and data center space. It also allows for better resource utilization, leading to overall cost efficiencies.
Can I run any operating system on a virtual machine?
Pretty much! The hypervisor’s capabilities will determine which OSes are supported, but many hypervisors support a wide range of operating systems, both server and desktop.