Cloud computing uses server virtualization a true b false – Cloud computing uses server virtualization: true or false? The answer is a resounding yes! Cloud computing, with its flexible and scalable nature, relies heavily on server virtualization. This technology allows multiple virtual servers to run on a single physical server, maximizing resource utilization and enabling the on-demand provisioning of resources that defines the cloud. We’ll explore how this fundamental relationship works, examining the benefits, challenges, and future trends in this dynamic field.
From Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) to Software as a Service (SaaS), server virtualization is the engine that powers the cloud’s efficiency. Imagine trying to manage thousands of individual physical servers—a logistical nightmare! Virtualization streamlines this, allowing for easy scaling, cost savings through resource optimization, and improved overall performance. This discussion will delve into the specifics, contrasting virtualization with alternative approaches and exploring security considerations within this critical infrastructure.
Server Virtualization in Cloud Computing
Server virtualization is the bedrock of modern cloud computing. It’s the technology that allows multiple virtual servers to run concurrently on a single physical server, dramatically changing how we manage and access computing resources. Without server virtualization, the cloud as we know it simply wouldn’t exist. It’s the engine that drives efficiency and scalability in cloud environments.Server virtualization enables cloud computing by abstracting the physical hardware from the operating systems and applications running on it.
This means that multiple virtual machines (VMs), each with its own operating system and resources, can share the same physical hardware resources like CPU, memory, and storage. This sharing leads to significant improvements in resource utilization and cost savings. Imagine a single, powerful server hosting hundreds of virtual servers, each dedicated to a different application or user, all operating independently and seemingly isolated from each other.
This is the power of virtualization.
Benefits of Server Virtualization in Cloud Environments
The advantages of using server virtualization in a cloud environment are numerous and impactful. These benefits translate directly to cost savings, increased efficiency, and improved scalability for cloud providers and their customers.Resource optimization is a key benefit. By consolidating multiple servers onto fewer physical machines, cloud providers reduce their hardware footprint, lowering energy consumption and data center space requirements.
This leads to significant cost savings in terms of hardware acquisition, maintenance, and energy bills. For example, a company might consolidate 10 physical servers into 3 virtualized servers, drastically reducing their energy and maintenance costs.Scalability is another significant advantage. Adding new virtual servers is a relatively quick and simple process, allowing cloud providers to easily scale their resources up or down based on demand.
This flexibility is crucial for handling fluctuating workloads and ensuring that resources are available when needed. A company experiencing a sudden surge in website traffic can instantly provision additional virtual servers to handle the increased load, preventing service disruptions.Cost efficiency is a direct consequence of resource optimization and scalability. By reducing hardware needs, energy consumption, and management overhead, cloud providers can offer computing resources at a lower cost to their customers.
This makes cloud computing a more attractive and accessible option for businesses of all sizes. The pay-as-you-go model of cloud computing, made possible by virtualization, further enhances cost efficiency by allowing customers to pay only for the resources they actually use.
Comparison of Server Virtualization Technologies
Several different server virtualization technologies are used in cloud computing, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The choice of technology often depends on factors like the specific needs of the cloud provider, the type of workloads being hosted, and the desired level of performance and security.One prominent technology is VMware vSphere, a widely adopted platform known for its robust features, mature ecosystem, and extensive management tools.
It provides a comprehensive virtualization solution for enterprise-level deployments. Hyper-V, developed by Microsoft, is another leading contender, tightly integrated with the Windows ecosystem and often preferred for Windows-based applications. It’s a strong competitor, offering a good balance of features and performance. Finally, KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) is an open-source solution that is gaining popularity due to its flexibility, performance, and cost-effectiveness.
It’s frequently used in Linux-based cloud environments and is a popular choice for providers seeking a cost-effective and customizable virtualization platform. The selection of a specific virtualization technology often depends on the overall architecture of the cloud environment and the preferences of the cloud provider.
The Relationship Between Cloud Computing and Server Virtualization
Cloud computing and server virtualization are deeply intertwined; one couldn’t realistically exist without the other at the scale we see today. Server virtualization is the foundational technology that makes the efficiency and scalability of cloud computing possible. Think of it like this: virtualization is the engine, and cloud computing is the car. The car can’t run without the engine, and the engine’s full potential is only realized when it’s part of a larger, functional system.Server virtualization allows multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run concurrently on a single physical server.
This dramatically increases resource utilization and reduces hardware costs. This efficiency is a cornerstone of cloud computing’s cost-effectiveness and on-demand scalability. Without virtualization, cloud providers would need vastly more physical hardware to deliver the same services, making cloud computing far more expensive and less accessible.
Server Virtualization’s Role in Cloud Infrastructure
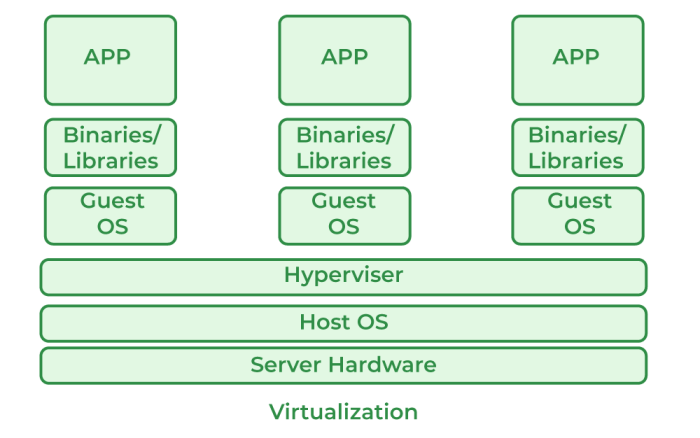
The following diagram illustrates how server virtualization underpins a typical cloud infrastructure:Imagine a box representing a physical server. Inside this box, several smaller boxes are nested, each representing a virtual machine. Each VM runs its own operating system and applications, completely isolated from the others. This isolation is crucial for security and resource management. Above the physical server box, you’d see a layer representing the cloud management platform, which manages and allocates resources to these VMs, responding to user demands.
The hypervisor, the software that enables virtualization, sits between the physical server and the VMs, orchestrating resource allocation and ensuring the VMs operate smoothly. This layered architecture is what allows for the dynamic allocation of resources and the efficient utilization of hardware, characteristics central to cloud computing.
Case Study: Netflix and Server Virtualization
Netflix, a prime example of a company heavily reliant on cloud computing, leverages server virtualization extensively. In its early days, Netflix relied on physical servers, leading to challenges in scaling its services to meet growing demand. The transition to a virtualized infrastructure allowed Netflix to dynamically provision resources, quickly scaling up or down based on viewing patterns. This agility is crucial for handling peak demand during popular show releases or holidays.
By using server virtualization, Netflix can efficiently manage its massive infrastructure, ensuring smooth streaming for millions of users globally while optimizing its hardware investment and operational costs. Their success is a testament to the power of server virtualization in enabling a robust and scalable cloud environment.
Security Considerations in Cloud Computing with Server Virtualization: Cloud Computing Uses Server Virtualization A True B False
Server virtualization, while offering significant benefits in cloud computing, introduces a new layer of security challenges. The shared nature of resources and the abstraction of hardware create vulnerabilities that need careful consideration and proactive mitigation strategies. Understanding these challenges is crucial for maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and applications within a virtualized cloud environment.The inherent complexities of virtualized server environments increase the attack surface.
A breach in one virtual machine (VM) could potentially compromise others on the same physical host, leading to a cascading effect. Moreover, the management and monitoring of numerous VMs adds complexity, making it challenging to identify and respond to security threats effectively. This necessitates a robust security framework tailored to the unique characteristics of cloud-based server virtualization.
Security Challenges in Virtualized Cloud Environments
Several significant security challenges arise from using server virtualization in cloud computing. These include the risk of VM escape, where a malicious actor gains control beyond the confines of a single VM to access the underlying hypervisor or other VMs. Another major concern is data breaches, potentially facilitated by misconfigurations or vulnerabilities within the hypervisor or virtual networking infrastructure.
Furthermore, the shared resources of a virtualized environment can create a single point of failure, where a compromise of a shared resource impacts multiple VMs. Finally, unauthorized access to management tools or hypervisor APIs can grant attackers significant control over the entire virtualized environment. Effective security strategies must address these vulnerabilities.
Best Practices for Securing Virtualized Servers in the Cloud, Cloud computing uses server virtualization a true b false
Implementing a comprehensive security strategy is vital for protecting virtualized servers in the cloud. This involves a multi-layered approach encompassing several key best practices. First, regular patching and updates are critical to address known vulnerabilities in both the hypervisor and guest operating systems. Second, robust access control mechanisms, such as role-based access control (RBAC), limit user privileges and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive resources.
Third, network segmentation isolates VMs and prevents lateral movement by attackers. Fourth, employing intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) helps monitor for suspicious activity and respond to threats in real-time. Fifth, regular security audits and penetration testing identify weaknesses and vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Sixth, implementing a strong disaster recovery plan ensures business continuity in case of a security incident.
Finally, data backups and encryption protect against data loss and unauthorized access.
Access Control and Encryption in Enhancing Security
Access control and encryption play a critical role in enhancing the security of virtualized servers in the cloud. Access control mechanisms, such as RBAC, define what actions users or applications can perform on specific resources. This limits the potential impact of a compromised account and prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data. Implementing strong authentication methods, like multi-factor authentication (MFA), adds an extra layer of security.
Encryption protects data both in transit and at rest, making it unreadable to unauthorized individuals even if a breach occurs. This includes encrypting virtual machine disks, network traffic, and data stored in cloud storage services. By combining robust access control with comprehensive encryption, organizations can significantly reduce their risk exposure.
In conclusion, the relationship between cloud computing and server virtualization is undeniable. Server virtualization isn’t just a component of cloud computing; it’s the backbone. Its ability to optimize resources, enhance scalability, and reduce costs is integral to the cloud’s success. While alternative approaches exist, they often lack the flexibility and efficiency offered by virtualization. As cloud computing continues to evolve, so too will server virtualization, paving the way for even more innovative and powerful cloud services.
FAQ
What are the main security risks associated with server virtualization in the cloud?
Security risks include vulnerabilities in the hypervisor, potential for unauthorized access to virtual machines, and data breaches if proper security measures aren’t implemented.
How does server virtualization impact the cost of cloud computing?
It significantly reduces costs by optimizing hardware usage, eliminating the need for many physical servers, and allowing for efficient resource allocation.
What are some examples of virtualization technologies used in cloud computing?
Popular examples include VMware vSphere, Microsoft Hyper-V, and KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine).
Is server virtualization necessary for all cloud services?
While it’s the dominant approach, some specialized cloud services might use alternative methods, but virtualization remains the cornerstone for most cloud infrastructure.